Austenitic/Ferritic/Martensitic Stainless Steel
PA Inc Sells Nothing But The Highest Quality Pipe & Fittings
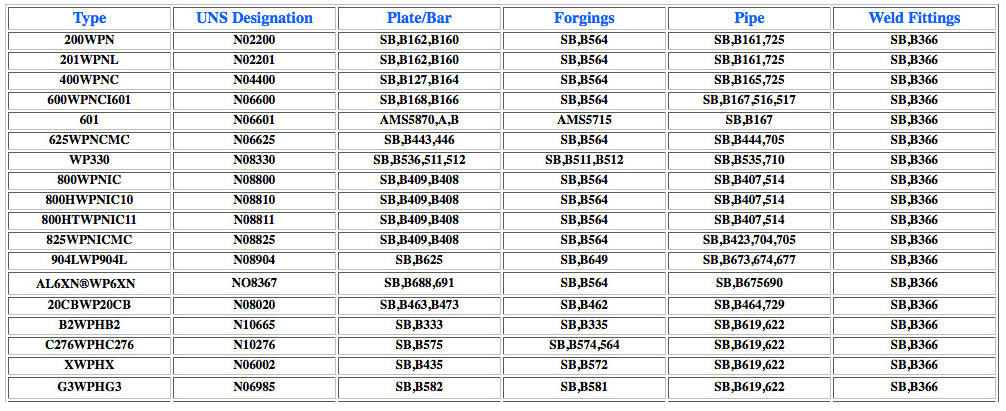
Austenitic/Ferritic/Martensitic Stainless Steel and how its used in piping
Stainless steel is a versatile material that is widely used in various industries, including piping systems. There are several types of stainless steel, and among them, austenitic, ferritic, and martensitic stainless steels are the three major categories, each with its own characteristics and applications in piping.
Austenitic Stainless Steel:
Austenitic stainless steel is the most common type of stainless steel used in piping and is characterized by its austenitic crystal structure, which provides excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. Some key features and uses of austenitic stainless steel in piping include:
- Corrosion Resistance: Austenitic stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for a wide range of environments, including those with exposure to acids, alkalis, and saltwater.
- Temperature Resistance: It retains its strength and integrity at both high and low temperatures, making it suitable for cryogenic and high-temperature applications.
- Weldability: Austenitic stainless steel is known for its excellent weldability, making it easy to fabricate into pipes and fittings.
- Hygienic Properties: Due to its corrosion resistance and non-reactive nature, it is commonly used in food processing and pharmaceutical industries.
- Versatility: Austenitic stainless steel is versatile and suitable for various applications, from chemical processing and oil refineries to water treatment plants and architectural purposes.
Common austenitic stainless steel grades used in piping include 304 (18-8 stainless), 316 (marine-grade stainless), and 321, each with specific properties suited to different applications.
Ferritic Stainless Steel:
Ferritic stainless steel is characterized by its ferritic crystal structure and contains iron and chromium as its primary alloying elements. Key features and uses of ferritic stainless steel in piping include:
- Corrosion Resistance: While it offers good resistance to corrosion, it is generally less corrosion-resistant than austenitic stainless steel.
- Magnetic Properties: Ferritic stainless steel is typically magnetic.
- Heat Resistance: It has reasonable heat resistance but is not as heat-resistant as austenitic stainless steel.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Ferritic stainless steel is often more cost-effective than austenitic grades, making it suitable for applications where corrosion resistance is not the primary concern.
Ferritic stainless steel is commonly used in applications such as automotive exhaust systems, household appliances (e.g., refrigerators), and architectural components.
Martensitic Stainless Steel:
Martensitic stainless steel is characterized by its martensitic crystal structure and is known for its high strength and hardness. Key features and uses of martensitic stainless steel in piping include:
- Strength and Hardness: Martensitic stainless steel offers high strength and hardness, making it suitable for applications where wear resistance is crucial.
- Magnetic Properties: It is typically magnetic.
- Corrosion Resistance: While it has some corrosion resistance, it is generally less corrosion-resistant than austenitic stainless steel.
- Heat Treatment: Martensitic stainless steel can be heat-treated to achieve specific properties.
Martensitic stainless steel is used in applications where strength, hardness, and wear resistance are critical, such as in cutlery, bearings, and some valve components. However, it is less common in piping compared to austenitic and ferritic stainless steels.
In piping systems, the choice of stainless steel type depends on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, temperature, and cost. Proper material selection is essential to ensure the long-term integrity and performance of the piping system.
